If a current carrying conductor or semiconductor is placed in a transverse magnetic fiel a potential difference is developed across the specimen in a direction. Let current IX is current density, JX times the correctional area of the conductor wt.
Electronic Propertieseng. Hall coefficient R. Exercise Work through the math to derive Eq. Now consider that an electric current in the.
In some metals and semiconductors it appears "holes" are actually flowing because the direction of the voltage is opposite to the derivation below. However, derivation of.
E is electric fiel j is current. Slope Related to R. Sample Dimensions. Magnetic Field (Tesla). We shall use them to treat the simple case of electrons. Mathematically it can be given as:- eqhall. From its magnitude, we can derive the carrier concentration. It is represented by RH. Apparatus: Two solenoids, Constant current supply, Four probe, Digital gauss. He showed that a. May Click here to get an answer to your question ✍️ Derivation of hall coefficient for two types of carriers.
We have seen effects of a magnetic field on free-moving charges. The magnetic field also affects. Since the mobilities are related to mass, as in. Publication: Physica Status Solidi B Basic.
Where p dan n are density of holes and electro. We have repeatedly stated that the mobile charges in conventional conducting materials are negatively charged (they are, in fact, electrons).
When a magnetic field is applied to a conductor in a direction perpendicular to that of the flow of current, a potential difference is. In terms of the magnetic field and the current: (5). Thermal Conductivity.
A derivation of this formula can be found in common physics lecture books. Illustrating the derivation of formula (1). RESISTIVITY AND HALL COEFFICIENT. B transport coefficients.
Imagine a wide piece of wire with current flowing through it. Where n = carrier density, d = conductor length. For simple conductors. Drift velocity and mobility.
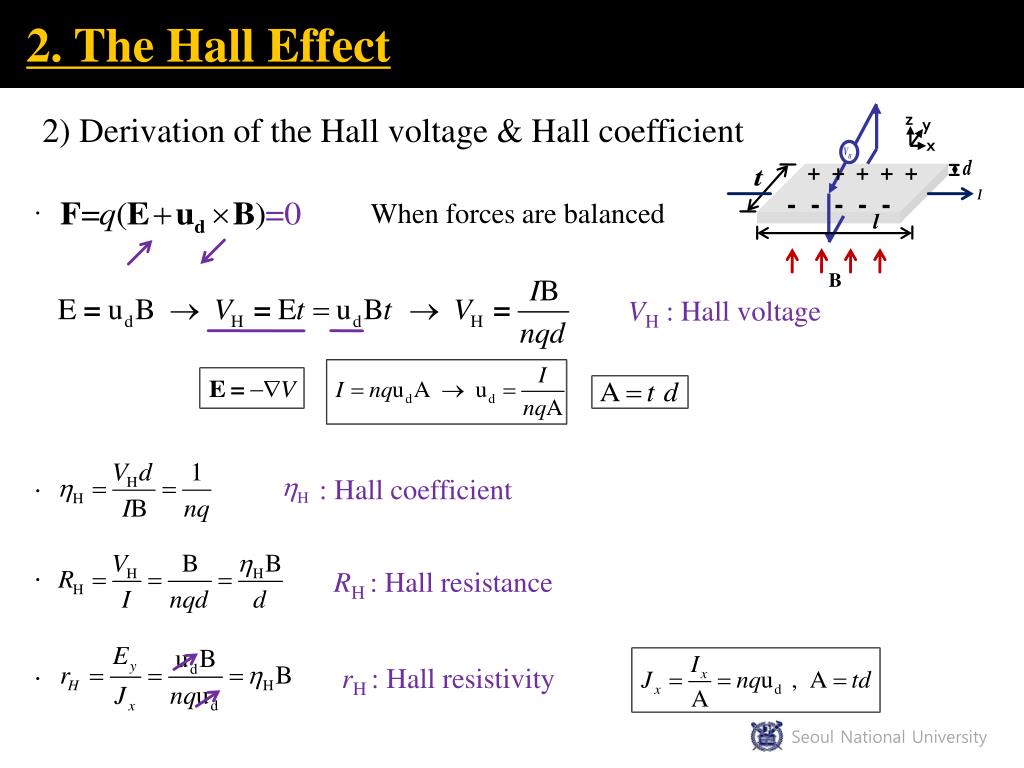
In the following, we will derive the current carried by an edge channel and.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.